Describe the Roles of Nucleic Acids Dna and Rna
Viruses use either DNA or RNA as genetic material but they require the hosts cellular machinery to replicate. DNA stores and transfers genetic information while RNA acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make amino acids and proteins.

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
DNA is an essential component required for transferring genes from parents to offspring.

. Nucleotides perform a wide variety of functions in the living cells besides being the building blocks or monomeric units in the nucleic acid DNA and RNA structure. DNA and RNA serve different functions. Discuss the mechanism and importance of DNA replication.
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA encodes the information the cell needs to make proteins. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. The entire genetic content of a cell is known as its genome.
The functions of nucleic acids have to do with the storage and expression of genetic information. A type of RNA called messenger RNA or mRNA reads DNA and makes a copy of it through a process called transcription. They consist of a strand of nucleotides with a phosphate group a 5 sugar and a nitrogenous base.
DNA carries the cells genetic blueprint and passes it on from parents to offspring in the form of chromosomes. Ribonucleic acid is an important nucleotide with long chains of nucleic acid present in all living cells. Describe nucleic acids structure and define the two types of nucleic acids Explain DNAs structure and.
By the end of this section you will be able to do the following. Sometimes RNA acts as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Ribonucleic acid RNA is a nucleic acid which is directly involved in protein synthesis.
They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Most of the DNA is located in the nucleus. DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms.
DNA along with RNA and proteins is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for life. Detection of microbial nucleic acids by the innate immune system is mediated by numerous intracellular nucleic acids sensors. Nucleic Acids and Heredity.
These include their role as structural components of some coenzymes of B-complex vitamins eg. 6 rows The sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA is oppositeNucleic acids mainly DNA and RNA play an. Define and describe DNA and RNA as polymers of nucleotides.
Nucleic Acid is responsible for the synthesis of protein in our body. 8 rows DNA is responsible for storing and transferring genetic information while RNA directly codes. FAD NAD in the energy reactions of cells ATP is the energy currency and in the control of metabolic reactions.
RNA is a vital component of protein synthesis. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are long chains polymers created by the joining of monomers which are the.
MRNA rRNA tRNA miRNA and siRNA. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The process of protein production involves two steps.
Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. In eukaryotic cells DNA forms a. MRNA carries this copy from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm where transfer RNA or tRNA helps to match amino acids to the code ultimately forming proteins through a process called translation.
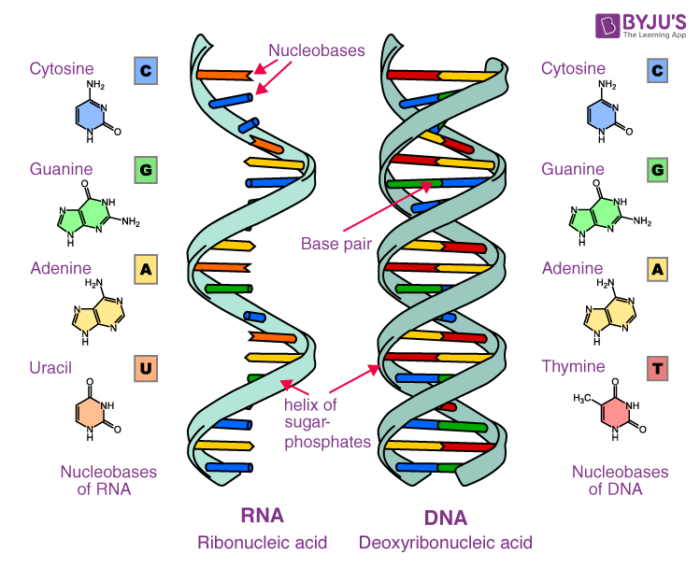
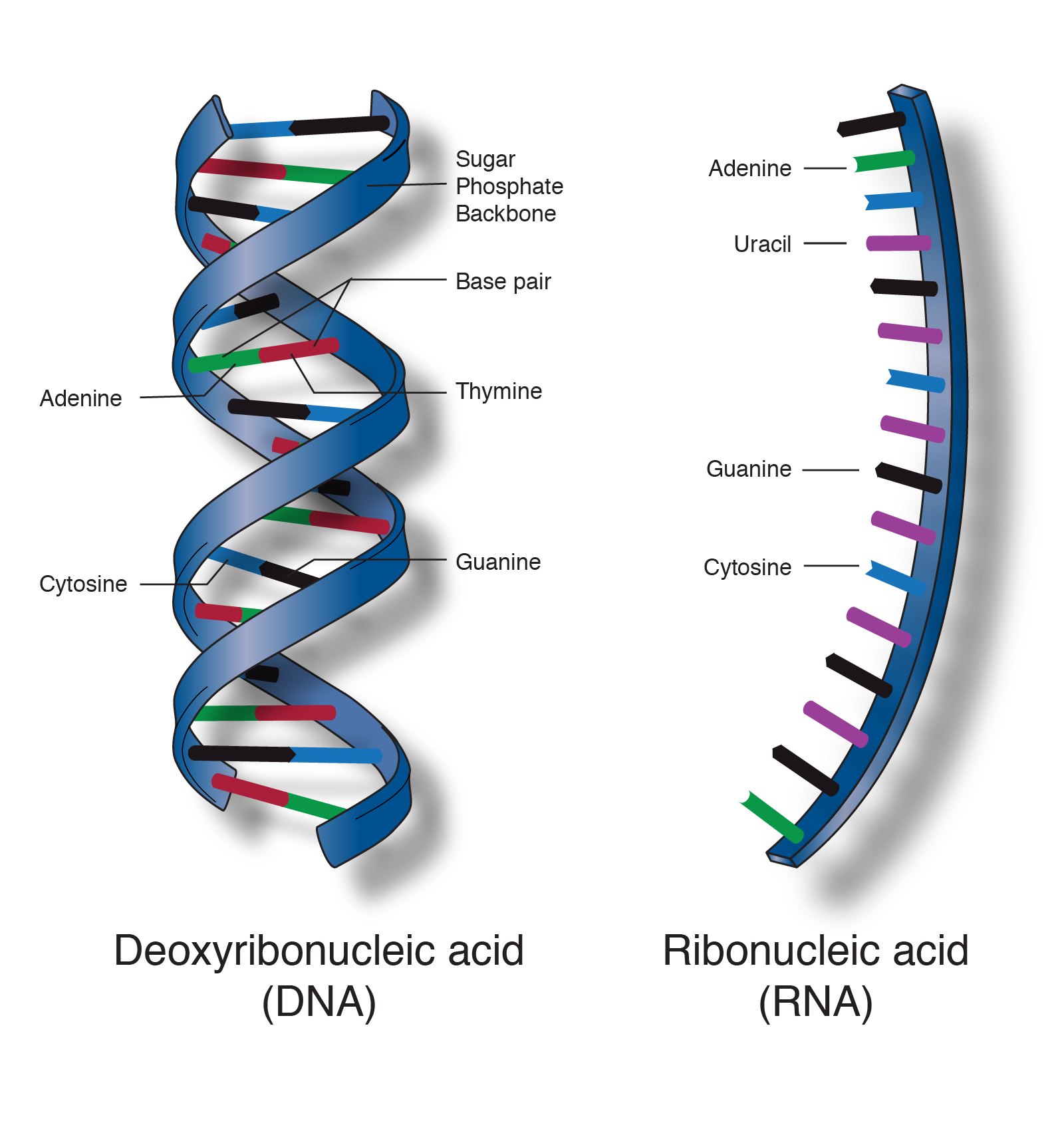
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA carries the sequence of coded instructions for the synthesis of proteins which are transcribed into ribonucleic acid RNA to be further translated into actual proteins. DNA and RNA Summary. It has a double-helical structure with the two strands running in opposite directions connected by hydrogen bonds and complementary to each other.
Upon the detection of nucleic acids these sensors induce the production of inflammatory cytokines and thus play a crucial role in the activation of anti-microbial immunity. Define the role of DNA in heredity and protein synthesis. 11 DNA basics structure.
All the information of a cell is stored in DNA. There are two types of nucleic acids. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids found in the cells of living organisms.
DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes and in the chloroplasts and mitochondria. In prokaryotes the DNA is not enclosed in a nucleus.
DNA makes RNA and RNA in return makes Protein. It starts the synthesis of peptide bonds by translating RNA information into protein information. Functions of Nucleic Acids.
DNA and RNA structure and function. Transfer genetic information from DNA to ribosomes. Describe ATP as an energy storage nucleotide.
Then for both the RNA and DNA sensing pathways we will identify the specific types of microbial infections that activate innate immune responses and how each microbe has evolved mechanisms to inhibit these pathways. Whilst DNA has the primary role. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA.
Loss of DNA content is linked to many diseases. Its main role is to act as a messenger conveying instructions from DNA for controlling the proteins synthesis. As such in this review we will describe the receptors of RNA and DNA nucleic acids and the signaling pathways that each stimulate.
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid is the genomic material in cells that contains the genetic information used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms. Describe the differences between DNA and RNA complementary base pairs. A related type of nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid RNA comes in different molecular forms that participate in protein synthesis.
Start studying DNA nucleic acids.
Nucleic Acids Definition Examples Functions Of Nucleic Acids
No comments for "Describe the Roles of Nucleic Acids Dna and Rna"
Post a Comment